
- Social Health Authority (SHA): Aiming for universal health coverage with significant hurdles to overcome.
- Mpox Outbreak: A new vaccine offers hope, but global inequities persist.
- Medical Intern Crisis: Strikes and systemic issues signal a need for better workforce management.
- Vaccination Drives: Progress in polio and malaria eradication efforts alongside controversies in livestock vaccination.
The year 2024 showcased an extraordinary mix of groundbreaking innovations and persistent health sector challenges, impacting millions across the globe. Below, we explore the year’s most notable developments and their broader implications.
Social Health Authority: Promise vs. Practicality
The Social Health Authority (SHA) was established on October 1, 2024, to advance Universal Health Coverage (UHC). Central to this initiative were the Social Health Insurance Fund (SHIF) and the Emergency, Chronic, and Critical Illness Fund (ECCIF). While these reforms were ambitious, their execution revealed substantial roadblocks:
- Reimbursement Delays: Healthcare providers struggled with slow payments, threatening service continuity.
- Limited Benefits: Citizens managing chronic conditions felt marginalized due to coverage gaps.
- Public Confusion: Integration issues between NHIF and SHIF led to widespread misinformation.

Moving forward, improved stakeholder engagement and streamlined operations are critical to SHA’s success.
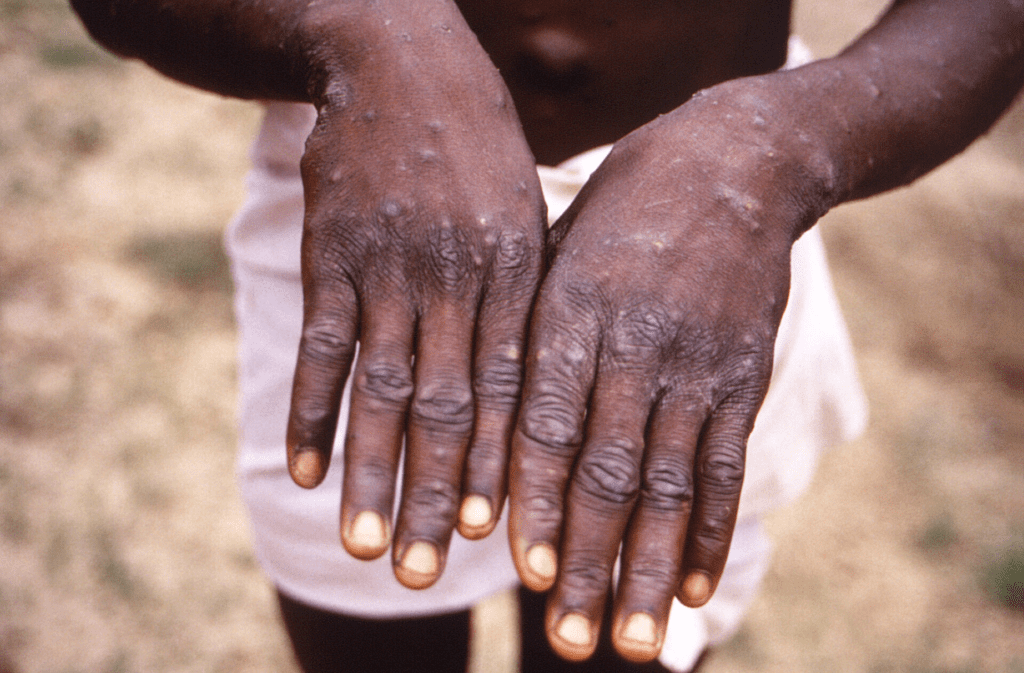
Mpox: A Persistent Global Threat
The mpox outbreak of May 2024, resulting in 31 confirmed cases across 12 counties, highlighted emerging infectious diseases. Key advancements included:
- Identification of two distinct viral clades.
- Approval of the MVA-BN vaccine, albeit with concerns about equitable distribution.
This episode reinforced the urgent need for proactive global collaboration to ensure vaccine accessibility and address health inequities.
Community Health Promoters: Progress and Pain Points
As pivotal agents of UHC, Community Health Promoters (CHPs) achieved remarkable milestones through the government’s Afya Nyumbani initiative. Successes included:
- Digital registration of 8.4 million households.
- Health screenings for over 37 million individuals.
- Improved access to child health assessments.
However, unresolved logistical challenges such as budgetary delays and network connectivity issues threaten the sustainability of these gains.
Medical Intern Crisis: A Wake-Up Call
Kenya’s medical intern crisis underscored systemic weaknesses in workforce management. Highlights included:
- Delayed Placements: Interns faced months-long waiting periods.
- Widespread Strikes: A two-month strike emphasized unresolved grievances.
- Salary Reductions: Pay cuts exacerbated morale issues.
The reinstatement of original salaries marked progress, but the situation called for structural reforms to ensure fair treatment and adequate support for healthcare workers.
Vaccination Drives: Achievements and Controversies
Kenya’s vaccination efforts in 2024 focused on two critical areas:
- Polio Eradication: Mass immunization campaigns vaccinated millions of children, countering outbreaks of Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus Type 2 (cVDPV2).
- Livestock Immunization: A nationwide program to vaccinate livestock faced public skepticism, underscoring the need for better communication and education.
These efforts highlighted the critical role of transparency and public trust in health initiatives.
Malaria Vaccine: A Historic Leap
The rollout of the R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine, developed by the University of Oxford and the Serum Institute of India, offered a groundbreaking solution to malaria, particularly in endemic regions. This innovation promises:
- Reduced childhood mortality rates.
- Improved disease management in sub-Saharan Africa.
This milestone emphasizes Africa’s leadership in adopting transformative health solutions.
Weight-Loss Medications: Balancing Innovation and Ethics
The diabetes drug Ozempic, repurposed for weight loss, spurred global demand and controversy. Key concerns included:
- Access Inequities: Diabetic patients faced shortages as the drug’s popularity for weight management surged.
- Ethical Debates: The prioritization of aesthetic over life-saving uses raised questions about equity.
Equitable distribution strategies must accompany medical innovation to ensure fairness.
Pig-to-Human Transplants: A Medical Breakthrough
The successful pig-to-human kidney transplant performed in March 2024 marked a significant advance in organ transplantation. By utilizing genetically modified pigs and CRISPR technology, scientists took a step closer to solving organ shortages. However, long-term viability and ethical considerations remain areas for ongoing exploration.
GMO Crops: Navigating Controversy
Kenya’s High Court upheld the reintroduction of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), enabling the commercialization of modified maize seeds. While proponents cited increased agricultural productivity, critics expressed concerns about environmental and health implications. Transparency and regulatory oversight are vital for this transition.
Cancer Vaccines: Personalized Treatment Revolution
mRNA-based cancer vaccines, developed with the same technology as Covid-19 vaccines, heralded a new era in oncology. These vaccines’ ability to target unique tumor markers offers:
- Improved treatment outcomes.
- Hope for individualized cancer care.
Affordability and widespread accessibility remain significant challenges.
AI in Maternal Healthcare: Bridging Rural Gaps
Jacaranda Health’s PROMPTS platform leveraged AI to enhance maternal care in underserved areas. Features included:
- Tailored pregnancy-related SMS reminders.
- Prioritization of high-risk cases using AI algorithms.
- Improved health outcomes for thousands of women.
This innovation underscores the potential of technology in addressing rural healthcare disparities.
The health sector in 2024 was a dynamic interplay of progress and persistent challenges. From innovative medical breakthroughs to systemic reforms, the year highlighted the importance of collaboration, transparency, and equitable resource distribution. As these trends continue, their long-term impact on global health will depend on sustained commitment to inclusive and innovative solutions.